3 MAJOR TRENDS IN BI AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS
November 22, 2016
Three major trends have been quietly impacting how organizations architect, design and leverage BI to enhance their customer experiences and to improve their operational efficiencies thus improving both top line and bottom line. These trends began even before the tsunami of Digital and Big Data took over the organizational mindshare but certainly have accelerated as a result of these and have since intertwined with them.
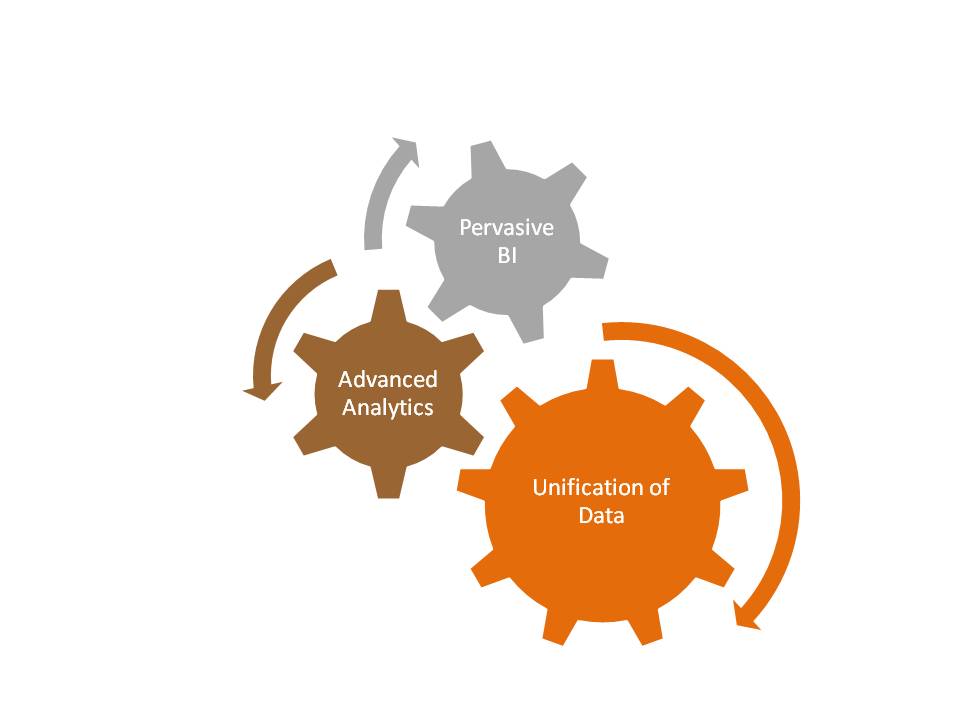
- Pervasive BI – Business Intelligence is no longer a back-office function that produced bulky PDF reports produced on a daily weekly or monthly basis and used to sit on users’ desktop until the next version came along. Actionable Business Intelligence is being introduced at every point of interaction be it external or internal stakeholders. When your call center representative is talking to your customers, does he or she have the intelligence required to delight the customer, when a buyer in a procurement department is placing an order for a raw material, does he have the intelligence to see if the raw material will arrive when it is needed as per the production schedule or likely quality of the material.Organizations with Pervasive BI are beginning to provide the call center agents to arm them with intelligence about calling a customer with the Next Best Action that will benefit both the customer and the organization. In the case of buyer, pervasive BI framework integrates supply chain analytics with the ERP system the buyer is using to enable him or her to intelligently make a decision about the timing, the vendor, and the right transit option so that the materials arrive when they are needed and are of right quality minimizing production delays and rejections thus improving operational efficiencies.There are several aspects of Pervasive BI for it to be meaningful and effective: Contextual self-service BI, integration with operational process or application, learns over time using machine learning algorithm. I’ll discuss these in greater detail in my next blog.
- Advanced Analytics – For Pervasive BI to be successful, we need to have advanced analytics capability that provides intelligence required at the point of interaction. This intelligence can come from predictive models that are adaptive and can be translated to simple actionable rules for specific situations at the time of interaction. These rules need to be easy to understand and be meaningful to provide guidance to call center agents and buyers in our previous examples. For this to be successful, organization need to be able to develop predictive models at much faster pace. Traditionally in most organizations, data scientists spend more than 70% of their time assembling and massaging data required for the models rather than building and enhancing models.
 The models also need to be updated (or better in self-learning mode) on a regular basis as new data flows in on an ongoing basis and feed insights from these models to pervasive BI that I talked about earlier. In the two examples, I used for pervasive BI.
The models also need to be updated (or better in self-learning mode) on a regular basis as new data flows in on an ongoing basis and feed insights from these models to pervasive BI that I talked about earlier. In the two examples, I used for pervasive BI.
- Unification of Data – Most structured data in organizations is scattered across several repositories. Moreover data in such repositories is not consistent due to several reasons including synchronization issues, data definition issues and applying different rules since each repository is populated by different data flows. Lack of pro-active and effective data governance to manage data across different repositories is a primary reason for such issues.
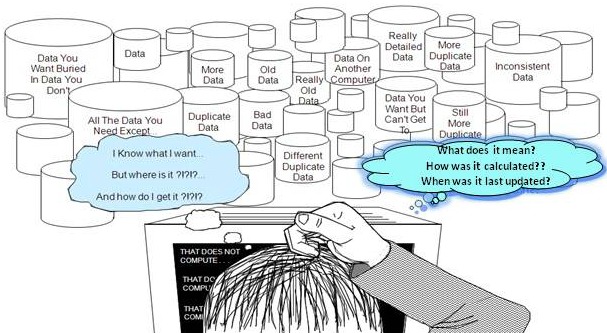 To compound the problem, organizations now have to deal with unstructured, streaming and IOT devices data (which together can be almost 80% of overall data).Many organizations are beginning to adopt Big Data Lakes to bring all kinds of data together. However, data lakes can easily turn into data swamps unless data is proactively governed and managed.
To compound the problem, organizations now have to deal with unstructured, streaming and IOT devices data (which together can be almost 80% of overall data).Many organizations are beginning to adopt Big Data Lakes to bring all kinds of data together. However, data lakes can easily turn into data swamps unless data is proactively governed and managed.

 English | EN
English | EN 