
As we are aware Jenkins pipeline is a set of plugins that are used for implementation and integration of the CI/CD process.
What is Continuous Integration?
Continuous Integration (CI) is a development practice that requires developers to integrate code into a shared repository several times a day. Each check-in is then verified by an automated build, allowing teams to detect problems early.
What is Continuous Delivery?
Continuous delivery is a software engineering approach in which teams produce software in short cycles, ensuring that the software can be reliably released at any time and, when releasing the software, doing so manually. It aims at building, testing, and releasing software with greater speed and frequency.
Jenkins MultiBranch pipeline allows us to automatically create a pipeline for each branch on your source control repository.
Multibranch pipeline works using along with Jenkinsfile that is usually stored along with our source code inside a version control repository.
In the previous blog, we already have seen how to work with Jenkinsfile. In this blog, I would be continuing with the same Jenkinsfile.
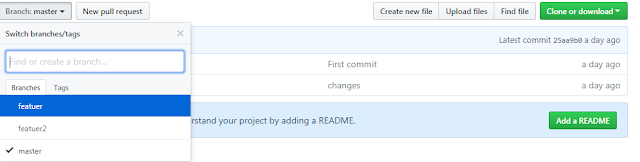
Before moving further, let’s check out the structure of my GIT Project.
Here as you can see I have created two feature branches name feature and feature2.
To Create Multibranch Jenkins Pipeline using Jenkinsfile we need to follow the below steps:
1) From Jenkins Home Page, Manage Jenkins–>Manage Plugin–>Install Pipeline Multibranch.

2) Now Click on Create New item, Provide Jenkins Job Name and Select Multibranch Pipeline Project.
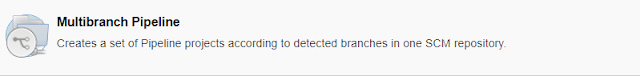
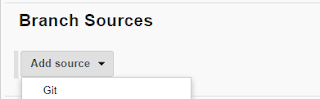
3) Under Branch Sources, Select GIT.
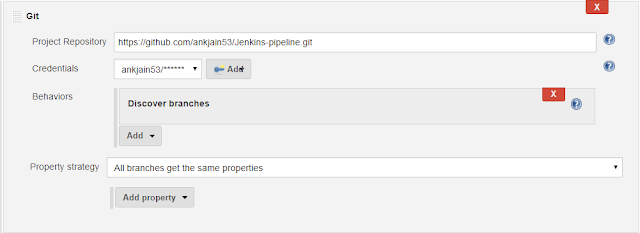
4) Now provide the path of your GIT repository.
5) Under Build Configuration Select path of Jenkinsfile.
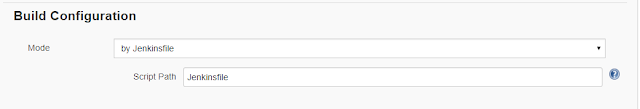
6) Click on Apply and Save Job.
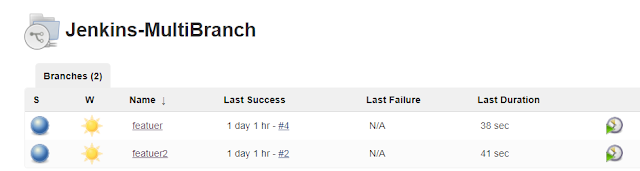
As we can see that in the above screenshot, corresponding to each branch in our GIT Repository different Jenkins job is automatically created and is getting executed in parallel. Even if we check-in any new branch in our Source code repository Jenkins will automatically identify it and create a new job automatically.

 English | EN
English | EN 